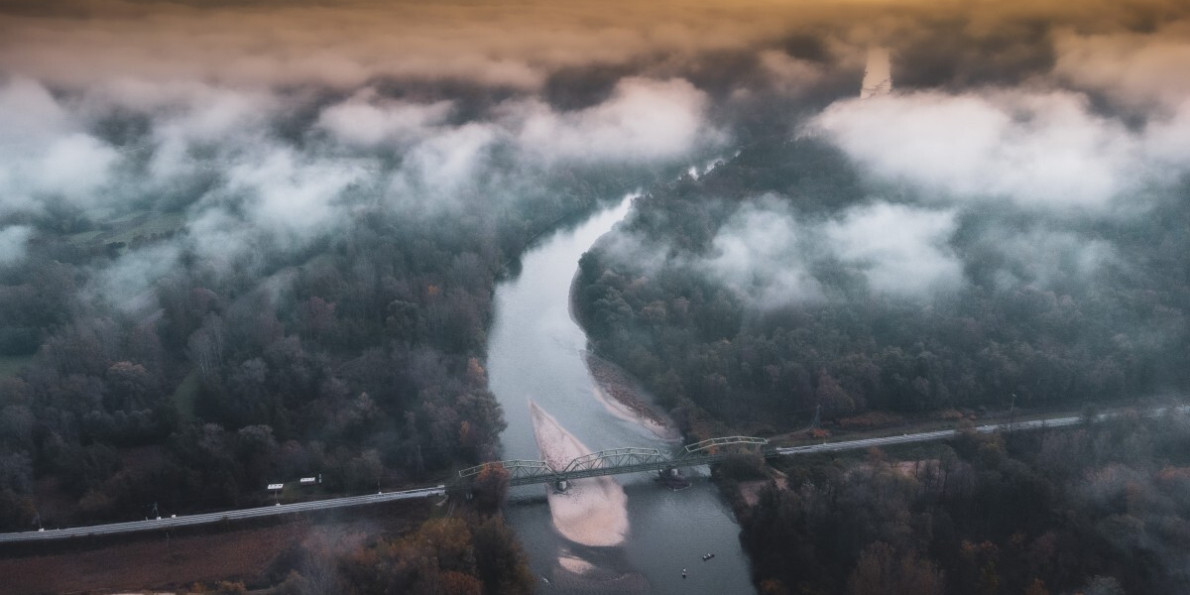
Mura river
The river in the lower stream winds and changes the stream, the cross -section (meander) and finds a shorter path. Water in the old riverbed remains, but no longer runs - this is how dead sleeves or dead .

For the use of social plugins such as Like, Share and Follow buttons. enable external cookies
eventually loses direct connection to the main riverbed and only high water flushes the dead, which thus ensures refreshment of living space and the relocation of plant and animal species. Under the guidance
- Her flood ecosystem with logs and meadows,
- Indigenous and non -compelling trees and plants,
- Rare and secured plants (daffodils),
- wood mushrooms,
- Diverse and rare birds (fountain, heron, black stork),
- Various dragonflies,
- Impact of the decline of groundwater and human intervention
Mura and her dead sleeves are an ecologically important and officially protected area and also the natural value of the national or of local importance. Given that the regulation of the Mura has been stopped by the hydrodynamic process, the preservation of the dead is more important, as new ones are not created at the moment, their flora and fauna are exceptional. In the municipality of Veržej, three areas related to the conservation of the river arch.
are subject to natural values.